 |
| A Man and his 42 pdr RML |
Its sited on a natural spit of land on the southern side of the harbour with a thoroughly commanding view of the approaches to Sydney Cove. It was one of three fortifications originally ordered, the others being Fort Macquarie (bottom right on the map below - which is now the site of the famous Sydney Opera House) and Fort Philip. Between them they could enfilade any ship entering the Cove.
(From: http://www.visitsydneyaustralia.com.au/harbour-forts.html)
Governor Arthur Phillip's first step was to fortify the entrance to Sydney Cove in 1788, as much to provide defence should there be a convict uprising as to engage any enemy ships that might came in close to the town in a hostile manner. He gave the task to Lieutenant William Dawes, an Officer of Engineers and Artillery in the detachment of Marines, who was instructed to build a simple mud redoubt for the storage of explosives. A similar fort was erected on Cattle Point (Bennelong Point)
In October 1788, HMS Supply was dispatched to the Cape of Good Hope to purchase much needed supplies. To make as much room as possible for the purchases which it was hoped it would bring back, eight guns were taken ashore and mounted at the Dawes Point fort, which was extended to accommodate the additional firepower. In the 1830s, a more permanent structure was built with five mortars, thirteen 42 pounder cannon, a magazine and quarters for a garrison of soldiers and their commanding officer. This fort remained intact until 1929 when the section above ground was demolished to make way for the Sydney Harbour Bridge.
 |
| Initial Battery layout with landed naval guns |
 |
| Diagram of the naval gun emplacement at the first battery |
 |
| Dawes Point from a early 1800s Sydney map |
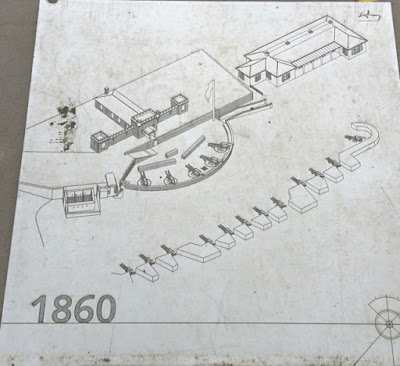 |
| The Crimean War sparked fears of raids by the Russian Pacific Fleet, and the fort was redeveloped and expanded . It also became the command post for the harbour defence network. |
 |
| With the expansion of outer harbour defences, the fort was reduced in size and obsolete guns decommissioned |
 |
| The battery was demolished in 1925 and by 1932 the new bridge was completed. |
The Upper Battery survived until demolition and is now directly under the pylons of the bridge (that the brick structure to the right of the remaining gun). You can see the remnants of the other gun platforms after their excavation around 10 years ago.
 |
| The surviving 42 pdr and carriage in the Upper Battery |
 |
| The commanding field of fire from the Upper Battery |
 |
| Dawes Pt Upper Battery circa 1875-1880 (pic from NSW Art Gallery) |
The Lower Battery
 |
| Lower Battery with 32 pdr RMLs (date unknown) |
 |
| Lower Battery emplacement today (with 42 pdr RML) |
 |
| Similarly commanding fields of fire over the centre of the harbour and the entrance to Sydney Cove |
Overall, a nice bit of colonial history tucked away under the bridge where you wont find it unless you know its there. Clearly a pivotal position for close defence of the colony both in its early days and throughout the Victorian era.
http://artilleryhistory.org/artillery_register/nsw/gun_dawes_point_sbml_42pdr_sn4.html
http://artilleryhistory.org/artillery_register/nsw/gun_dawes_point_sbml_42pdr_sn3.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dawes_Point_Battery
http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/heritageapp/visit/ViewAttractionDetail.aspx?ID=5053114
http://www.doryanthes.info/pdf/Dawes%20Point%20Excavation.pdf






























